A class used to test the Hypercube class. More...
Classes | |
| enum | Infinity |
| Variables are used to determine whether infinite values are allowed. More... | |
Public Member Functions | |
| HypercubeTest (String name) | |
| Contructor that returns a TestCase consisting of a single test method. | |
| void | setUp () |
| void | testSaveAsXMLRandom () |
| Tests the saving to XML functionality. | |
| void | testEqualClonesRandom () |
| Tests that a hypercube is equal to a clone of itself. | |
| void | testEquivalentRandom () |
| Tests that a hypercube is equivalent to itself with reordered variables. | |
| void | testJoinRandom () |
| This method creates random number of hypercubes and then first join the hypercubes with one call of the join method. | |
| void | testApplyJoinRandom () |
| This method creates two random hypercubes change the variables order of the second hypercube so that the variables order of the two hypercubes is not necessarily consistent, then joins these two hypercubes by using join and applyJoin methods, and compares the two outputs. | |
| void | testProjectionRandom () |
| This method creates two random hypercubes and an array of random variables obtained from the variables of each hypercube. | |
| void | testApplyProjectRandom () |
| This method creates a random hypercube and a random array of variables, then checks that the result of the projection of these variables out of the hypercube by using project and applyProject is the same. | |
| void | testProjOutputRandom () |
| This method tests that the projection method (taking a list of variables) computes the correct optimal assignments. | |
| void | testProjOutputRandom2 () |
| This method tests that the projection method (taking a number of variables) computes the correct optimal assignments. | |
| void | testSliceRandom () |
| This method creates two random hypercubes, performs a slice on them, and them joins the two sliced hypercubes. | |
| void | testApplySliceRandom () |
| Creates one random hypercube and tests if slice and applySlice return the same output. | |
| void | testSplittingRandom () |
| this method creates a random hypercube. | |
| void | testChangeVariablesOrderRandom () |
| Tests changing the order of variables. | |
| void | testApplyChangeVariablesOrderRandom () |
| creates a random hypercube and tests whether changeVariablesOrder and applyChangeVariablesOrder return the same output | |
| void | testGetUtility () |
| This method creates a random hypercube, then gets all its utilities values and store them in a new arrray, and finally checks this array is identical to the utilities array of the original hypercube. | |
| void | testProjection () |
| Tests the projection methods on a simple example. | |
| void | testSerializationRandom () throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException |
| Tests the serialization of a random hypercube. | |
| void | testSerializationNullHypercube () |
| Method to test the serialization of the NULL hypercube. | |
| void | testUnion () |
| Tests the union() method. | |
| void | testProjectAllRandom () |
| Tests the projection method when all variables are projected out. | |
| void | testBlindProjectRandom () |
| Tests blindProject(). | |
| void | testSmartJoinRandom () |
| Tests the additive join method that automatically computes the variable ordering. | |
| void | testSmartMultiplyRandom () |
| Tests the multiplicative join method that automatically computes the variable ordering. | |
| void | testSmartJoinRandom (boolean addition) |
| Tests the join method that automatically computes the variable ordering. | |
| void | testExpectation () |
| Tests the expectation operation. | |
| void | testCompose () |
| Tests the composition method. | |
| void | testSample () |
| Test for the sample(int) method. | |
| void | testConsensusWeighted () |
| Tests the consensus() operation with weighted samples. | |
| void | testConsensusWeightedExpect () |
| Tests the consensusExpect() operation with weighted samples. | |
| void | testIterator () |
| Test for the iterator() method that takes in a list of variables not necessarily containing all the space's variables. | |
Static Public Member Functions | |
| static Test | suite () |
| Builds up a test suite. | |
| static Hypercube< AddableInteger, AddableInteger > | random_hypercube () |
| static Hypercube< AddableInteger, AddableInteger > | random_hypercube (double prob) |
| static< U extends Addable< U > Hypercube< AddableInteger, U > | random_hypercube (double prob, Class< U > utilClass) |
| static Hypercube< AddableInteger, AddableInteger > | random_hypercube (int number_variables, int domain_size, int redundancy, int shift) |
| static Hypercube< AddableInteger, AddableInteger > | random_hypercube (int number_variables, int domain_size, int redundancy, int shift, AddableInteger infeasibleUtil) |
| static< U extends Addable< U > Hypercube< AddableInteger, U > | random_hypercube (int number_variables, int domain_size, int redundancy, int shift, U infeasibleUtil, Class< U > utilClass) |
Public Attributes | |
| boolean | maximize |
| This variable is used to choose between maximising and minimising during the tests. | |
Static Public Attributes | |
| static Infinity | inf = Infinity.NONE |
| This variable is used to make sure that one does not mix plus infinity and min infinity in the testing. | |
Package Functions | |
| private< T extends Comparable< T > > T[] | intersection (T[] array1, T[] array2) |
| Computes the intersection of two lists. | |
Private Member Functions | |
| void | verifyProjection (Hypercube< AddableInteger, AddableInteger > hypercube, UtilitySolutionSpace.ProjOutput< AddableInteger, AddableInteger > projOutput, String[] vars) |
| Verifies the output of the projection method. | |
| String[] | sub_variables (String[] variables) |
| Computes a random sublist of the input list of variables. | |
| String[] | union (String[] array1, String[] array2, String[] total_variables) |
| Computes the union of two lists, respecting the input total order on the elements. | |
| void | testConsensusWeighted (final boolean expect) |
| Tests the consensus() operation with weighted samples. | |
Detailed Description
A class used to test the Hypercube class.
- Todo
- change every test in the following manner. If it fails, log the arguments and information what has failed so the test can be repeated.
Constructor & Destructor Documentation
◆ HypercubeTest()
| frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.tests.HypercubeTest.HypercubeTest | ( | String | name | ) |
Contructor that returns a TestCase consisting of a single test method.
- Parameters
-
name the name of the method to be used
Referenced by suite().
Member Function Documentation
◆ intersection()
|
package |
Computes the intersection of two lists.
- Parameters
-
<T> the type of the elements in the lists array1 the first list array2 the second list
- Returns
- the intersection of the two lists
References intersection().
Referenced by intersection(), and testSliceRandom().

◆ random_hypercube() [1/6]
|
static |
- Returns
- a random hypercube
References random_hypercube().
Referenced by random_hypercube(), random_hypercube(), random_hypercube(), random_hypercube(), random_hypercube(), testApplyChangeVariablesOrderRandom(), testApplyJoinRandom(), testApplyProjectRandom(), testApplySliceRandom(), testBlindProjectRandom(), testChangeVariablesOrderRandom(), testCompose(), testConsensusWeighted(), testEqualClonesRandom(), testEquivalentRandom(), testExpectation(), testGetUtility(), testIterator(), testJoinRandom(), frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.tests.HypercubeIterBestFirstTest.testMaximize(), frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.tests.HypercubeIterBestFirstTest.testMinimize(), frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.tests.HypercubeIterTest.testMoreVars(), frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.tests.HypercubeIterTest.testOtherOrder(), testProjectAllRandom(), testProjectionRandom(), testProjOutputRandom(), testProjOutputRandom2(), frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.tests.HypercubeIterTest.testSameOrder(), testSaveAsXMLRandom(), testSerializationRandom(), testSliceRandom(), testSmartJoinRandom(), testSplittingRandom(), and frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.tests.HypercubeIterTest.testSubDoms().

◆ random_hypercube() [2/6]
|
static |
- Parameters
-
prob for any given utility, the probability that it be infinite
- Returns
- random hypercube
- Todo
- This implementation is too restrictive (imposes an order on variables, values...).
References random_hypercube().
◆ random_hypercube() [3/6]
|
static |
- Parameters
-
<U> the class used for utility values prob for any given utility, the probability that it be infinite utilClass the class used for utility values
- Returns
- random hypercube
- Todo
- This implementation is too restrictive (imposes an order on variables, values...).
References inf, frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.tests.HypercubeTest.Infinity.NONE, and frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.tests.HypercubeTest.Infinity.PLUS_INFINITY.
◆ random_hypercube() [4/6]
|
static |
- Parameters
-
number_variables number of variables of the generated Hypercube will contain domain_size number of values that the domains of the variables of the Hypercube redundancy redundancy in the array of utilities (between 0 - 100) shift the number starting with which the variables should be named (Xshift, X(shift+1)...)
- Returns
- a random hypercube, with some random utilities set to -1
References random_hypercube().
◆ random_hypercube() [5/6]
|
static |
- Parameters
-
number_variables number of variables of the generated Hypercube will contain domain_size number of values that the domains of the variables of the Hypercube redundancy redundancy in the array of utilities (between 0 - 100) shift the number starting with which the variables should be named (Xshift, X(shift+1)...) infeasibleUtil the infeasible utility
- Returns
- a random hypercube, with some random utilities set to -1
References random_hypercube().
◆ random_hypercube() [6/6]
|
static |
- Parameters
-
<U> the type of utility values number_variables number of variables of the generated Hypercube will contain domain_size number of values that the domains of the variables of the Hypercube redundancy redundancy in the array of utilities (between 0 - 100) shift the number starting with which the variables should be named (Xshift, X(shift+1)...) infeasibleUtil the infeasible utility utilClass the type of utility values
- Returns
- a random hypercube, with some random utilities set to -1
variables names and their domains ///
array of utilities ///
References random_hypercube().
◆ setUp()
| void frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.tests.HypercubeTest.setUp | ( | ) |
- See also
- junit.framework.TestCase#setUp()
References inf, maximize, frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.tests.HypercubeTest.Infinity.MIN_INFINITY, frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.tests.HypercubeTest.Infinity.NONE, and frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.tests.HypercubeTest.Infinity.PLUS_INFINITY.
◆ sub_variables()
|
private |
Computes a random sublist of the input list of variables.
- Parameters
-
variables list of variables
- Returns
- a random sublist of variables
References sub_variables().
Referenced by sub_variables(), testApplyProjectRandom(), testProjectionRandom(), and testSplittingRandom().

◆ suite()
|
static |
Builds up a test suite.
- Returns
- a TestSuite in which randomized test methods are run multiple times, and others only once
References HypercubeTest().
Referenced by frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.tests.AllTestsHypercube.suite().

◆ testApplyChangeVariablesOrderRandom()
| void frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.tests.HypercubeTest.testApplyChangeVariablesOrderRandom | ( | ) |
creates a random hypercube and tests whether changeVariablesOrder and applyChangeVariablesOrder return the same output
References frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.Hypercube< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Addable< U > >.changeVariablesOrder(), frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.Hypercube< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Addable< U > >.clone(), frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.Hypercube< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Addable< U > >.equals(), and random_hypercube().
◆ testApplyJoinRandom()
| void frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.tests.HypercubeTest.testApplyJoinRandom | ( | ) |
This method creates two random hypercubes change the variables order of the second hypercube so that the variables order of the two hypercubes is not necessarily consistent, then joins these two hypercubes by using join and applyJoin methods, and compares the two outputs.
References frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.Hypercube< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Addable< U > >.applyJoin(), frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.Hypercube< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Addable< U > >.changeVariablesOrder(), frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.Hypercube< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Addable< U > >.clone(), frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.Hypercube< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Addable< U > >.join(), and random_hypercube().
◆ testApplyProjectRandom()
| void frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.tests.HypercubeTest.testApplyProjectRandom | ( | ) |
This method creates a random hypercube and a random array of variables, then checks that the result of the projection of these variables out of the hypercube by using project and applyProject is the same.
References frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.Hypercube< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Addable< U > >.applyProject(), frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.Hypercube< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Addable< U > >.clone(), maximize, frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.Hypercube< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Addable< U > >.project(), random_hypercube(), frodo2.solutionSpaces.UtilitySolutionSpace< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Addable< U > >.ProjOutput< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Addable< U > >.space, sub_variables(), and verifyProjection().
◆ testApplySliceRandom()
| void frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.tests.HypercubeTest.testApplySliceRandom | ( | ) |
Creates one random hypercube and tests if slice and applySlice return the same output.
References frodo2.solutionSpaces.AddableInteger.add(), frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.Hypercube< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Addable< U > >.equals(), random_hypercube(), and frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.Hypercube< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Addable< U > >.slice().
◆ testBlindProjectRandom()
| void frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.tests.HypercubeTest.testBlindProjectRandom | ( | ) |
Tests blindProject().
References frodo2.java, maximize, and random_hypercube().
◆ testChangeVariablesOrderRandom()
| void frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.tests.HypercubeTest.testChangeVariablesOrderRandom | ( | ) |
Tests changing the order of variables.
References frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.Hypercube< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Addable< U > >.changeVariablesOrder(), frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.Hypercube< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Addable< U > >.equals(), and random_hypercube().

◆ testCompose()
| void frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.tests.HypercubeTest.testCompose | ( | ) |
Tests the composition method.
References frodo2.solutionSpaces.AddableInteger.add(), frodo2.solutionSpaces.BasicUtilitySolutionSpace< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Serializable >.changeVariablesOrder(), frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.BasicHypercube< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Serializable >.changeVariablesOrder(), frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.BasicHypercube< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Serializable >.equivalent(), frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.BasicHypercube< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Serializable >.getDomain(), frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.BasicHypercube< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Serializable >.getNumberOfVariables(), frodo2.solutionSpaces.BasicUtilitySolutionSpace< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Serializable >.getUtility(), frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.BasicHypercube< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Serializable >.getUtility(), frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.BasicHypercube< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Serializable >.getVariables(), inf, frodo2.solutionSpaces.AddableInteger.MinInfinity.MIN_INF, frodo2.solutionSpaces.AddableInteger.PlusInfinity.PLUS_INF, frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.tests.HypercubeTest.Infinity.PLUS_INFINITY, random_hypercube(), and testCompose().
Referenced by testCompose().
◆ testConsensusWeighted() [1/2]
| void frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.tests.HypercubeTest.testConsensusWeighted | ( | ) |
Tests the consensus() operation with weighted samples.
References testConsensusWeighted().
Referenced by testConsensusWeighted(), and testConsensusWeightedExpect().

◆ testConsensusWeighted() [2/2]
|
private |
Tests the consensus() operation with weighted samples.
- Parameters
-
expect whether to compose the consensus operation with the expectation operation
References frodo2.solutionSpaces.UtilitySolutionSpace< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Addable< U > >.ProjOutput< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Addable< U > >.assignments, frodo2.solutionSpaces.UtilitySolutionSpace< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Addable< U > >.blindProject(), frodo2.solutionSpaces.UtilitySolutionSpace< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Addable< U > >.changeVariablesOrder(), frodo2.solutionSpaces.AddableReal.compareTo(), frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.Hypercube< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Addable< U > >.compose(), frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.Hypercube< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Addable< U > >.consensus(), frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.Hypercube< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Addable< U > >.consensusAllSols(), frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.Hypercube< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Addable< U > >.consensusExpect(), frodo2.solutionSpaces.UtilitySolutionSpace< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Addable< U > >.expectation(), frodo2.solutionSpaces.BasicUtilitySolutionSpace< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Serializable >.SparseIterator< V, U >.getCurrentUtility(), frodo2.solutionSpaces.SolutionSpace< V extends Addable< V > >.getDomain(), frodo2.solutionSpaces.SolutionSpace< V extends Addable< V > >.getNumberOfSolutions(), frodo2.solutionSpaces.SolutionSpace< V extends Addable< V > >.getNumberOfVariables(), frodo2.solutionSpaces.BasicUtilitySolutionSpace< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Serializable >.getUtility(), frodo2.solutionSpaces.SolutionSpace< V extends Addable< V > >.getVariables(), frodo2.solutionSpaces.UtilitySolutionSpace< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Addable< U > >.ProjOutput< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Addable< U > >.getVariables(), frodo2.solutionSpaces.SolutionSpace< V extends Addable< V > >.Iterator< V >.hasNext(), frodo2.solutionSpaces.UtilitySolutionSpace< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Addable< U > >.iterator(), maximize, frodo2.solutionSpaces.UtilitySolutionSpace< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Addable< U > >.multiply(), frodo2.solutionSpaces.BasicUtilitySolutionSpace< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Serializable >.SparseIterator< V, U >.nextUtility(), frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.Hypercube< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Addable< U > >.NullHypercube< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Addable< U > >.NULL, random_hypercube(), frodo2.solutionSpaces.UtilitySolutionSpace< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Addable< U > >.resolve(), frodo2.solutionSpaces.BasicUtilitySolutionSpace< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Serializable >.slice(), frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.Hypercube< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Addable< U > >.slice(), frodo2.solutionSpaces.UtilitySolutionSpace< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Addable< U > >.slice(), and frodo2.solutionSpaces.UtilitySolutionSpace< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Addable< U > >.ProjOutput< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Addable< U > >.space.
◆ testConsensusWeightedExpect()
| void frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.tests.HypercubeTest.testConsensusWeightedExpect | ( | ) |
Tests the consensusExpect() operation with weighted samples.
References testConsensusWeighted().
◆ testEqualClonesRandom()
| void frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.tests.HypercubeTest.testEqualClonesRandom | ( | ) |
Tests that a hypercube is equal to a clone of itself.
References frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.Hypercube< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Addable< U > >.clone(), frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.Hypercube< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Addable< U > >.equals(), and random_hypercube().
◆ testEquivalentRandom()
| void frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.tests.HypercubeTest.testEquivalentRandom | ( | ) |
Tests that a hypercube is equivalent to itself with reordered variables.
References frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.Hypercube< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Addable< U > >.changeVariablesOrder(), and random_hypercube().

◆ testExpectation()
| void frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.tests.HypercubeTest.testExpectation | ( | ) |
Tests the expectation operation.
References frodo2.solutionSpaces.AddableReal.add(), frodo2.solutionSpaces.AddableReal.doubleValue(), frodo2.solutionSpaces.AddableReal.equals(), frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.Hypercube< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Addable< U > >.expectation(), frodo2.solutionSpaces.SolutionSpace< V extends Addable< V > >.SparseIterator< V >.getCurrentSolution(), frodo2.solutionSpaces.BasicUtilitySolutionSpace< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Serializable >.SparseIterator< V, U >.getCurrentUtility(), frodo2.solutionSpaces.SolutionSpace< V extends Addable< V > >.Iterator< V >.getNbrSolutions(), frodo2.solutionSpaces.SolutionSpace< V extends Addable< V > >.Iterator< V >.hasNext(), frodo2.solutionSpaces.UtilitySolutionSpace< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Addable< U > >.iterator(), frodo2.solutionSpaces.UtilitySolutionSpace< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Addable< U > >.join(), frodo2.solutionSpaces.UtilitySolutionSpace< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Addable< U > >.multiply(), frodo2.solutionSpaces.BasicUtilitySolutionSpace< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Serializable >.SparseIterator< V, U >.nextUtility(), random_hypercube(), frodo2.solutionSpaces.UtilitySolutionSpace< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Addable< U > >.resolve(), and frodo2.solutionSpaces.UtilitySolutionSpace< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Addable< U > >.slice().
◆ testGetUtility()
| void frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.tests.HypercubeTest.testGetUtility | ( | ) |
This method creates a random hypercube, then gets all its utilities values and store them in a new arrray, and finally checks this array is identical to the utilities array of the original hypercube.
References frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.Hypercube< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Addable< U > >.getUtility(), and random_hypercube().
◆ testIterator()
| void frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.tests.HypercubeTest.testIterator | ( | ) |
Test for the iterator() method that takes in a list of variables not necessarily containing all the space's variables.
- Todo
- Further tests could be useful.
References frodo2.solutionSpaces.SolutionSpace< V extends Addable< V > >.SparseIterator< V >.getVariablesOrder(), frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.Hypercube< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Addable< U > >.iterator(), and random_hypercube().
◆ testJoinRandom()
| void frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.tests.HypercubeTest.testJoinRandom | ( | ) |
This method creates random number of hypercubes and then first join the hypercubes with one call of the join method.
then join the hypercube two by two and compare the two results.
References frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.Hypercube< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Addable< U > >.join(), frodo2.solutionSpaces.UtilitySolutionSpace< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Addable< U > >.join(), random_hypercube(), and testJoinRandom().
Referenced by testJoinRandom().
◆ testProjectAllRandom()
| void frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.tests.HypercubeTest.testProjectAllRandom | ( | ) |
Tests the projection method when all variables are projected out.
References frodo2.solutionSpaces.AddableInteger.compareTo(), maximize, and random_hypercube().

◆ testProjection()
| void frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.tests.HypercubeTest.testProjection | ( | ) |
Tests the projection methods on a simple example.
References frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.Hypercube< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Addable< U > >.equals(), and frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.Hypercube< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Addable< U > >.project().
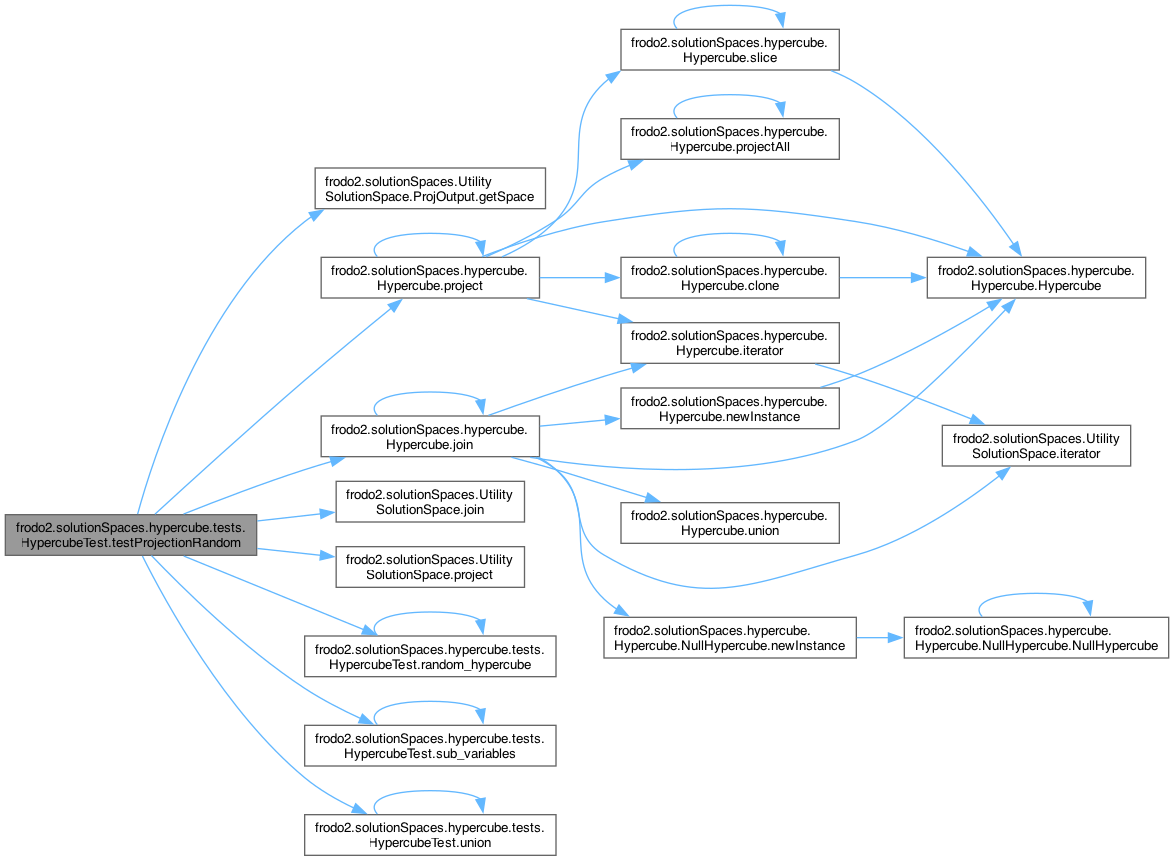
◆ testProjectionRandom()
| void frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.tests.HypercubeTest.testProjectionRandom | ( | ) |
This method creates two random hypercubes and an array of random variables obtained from the variables of each hypercube.
then it projects from the two hypercubes the two random arrays of variables and joins the resulting hypercubes. It compares the result obtained with the one obtained if the join operation is done first.
References frodo2.solutionSpaces.UtilitySolutionSpace< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Addable< U > >.ProjOutput< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Addable< U > >.getSpace(), frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.Hypercube< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Addable< U > >.join(), frodo2.solutionSpaces.UtilitySolutionSpace< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Addable< U > >.join(), maximize, frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.Hypercube< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Addable< U > >.project(), frodo2.solutionSpaces.UtilitySolutionSpace< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Addable< U > >.project(), random_hypercube(), sub_variables(), and union().
◆ testProjOutputRandom()
| void frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.tests.HypercubeTest.testProjOutputRandom | ( | ) |
This method tests that the projection method (taking a list of variables) computes the correct optimal assignments.
References maximize, random_hypercube(), and verifyProjection().
◆ testProjOutputRandom2()
| void frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.tests.HypercubeTest.testProjOutputRandom2 | ( | ) |
This method tests that the projection method (taking a number of variables) computes the correct optimal assignments.
References maximize, random_hypercube(), and verifyProjection().
◆ testSample()
| void frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.tests.HypercubeTest.testSample | ( | ) |
Test for the sample(int) method.
References frodo2.solutionSpaces.AddableReal.PlusInfinity.PLUS_INF, and frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.Hypercube< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Addable< U > >.sample().

◆ testSaveAsXMLRandom()
| void frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.tests.HypercubeTest.testSaveAsXMLRandom | ( | ) |
Tests the saving to XML functionality.
References frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.Hypercube< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Addable< U > >.equals(), random_hypercube(), and frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.Hypercube< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Addable< U > >.saveAsXML().
◆ testSerializationNullHypercube()
| void frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.tests.HypercubeTest.testSerializationNullHypercube | ( | ) |
Method to test the serialization of the NULL hypercube.
Constructor
- Parameters
-
out the output stream obj the object to be written
- Bug
- objIn might not be closed
References frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.Hypercube< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Addable< U > >.equals(), frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.Hypercube< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Addable< U > >.NullHypercube< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Addable< U > >.NULL, and testSerializationNullHypercube().
Referenced by testSerializationNullHypercube().
◆ testSerializationRandom()
| void frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.tests.HypercubeTest.testSerializationRandom | ( | ) | throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException |
Tests the serialization of a random hypercube.
- Exceptions
-
IOException if unable to create the pipes, or an I/O error occurs when deserializing the hypercube ClassNotFoundException should never happen
Constructor
- Parameters
-
out the output stream obj the object to be written
References frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.Hypercube< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Addable< U > >.equals(), random_hypercube(), and testSerializationRandom().
Referenced by testSerializationRandom().
◆ testSliceRandom()
| void frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.tests.HypercubeTest.testSliceRandom | ( | ) |
This method creates two random hypercubes, performs a slice on them, and them joins the two sliced hypercubes.
It compares the result with the one obtained if the join is performed first.
References frodo2.solutionSpaces.AddableInteger.add(), frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.Hypercube< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Addable< U > >.equals(), intersection(), frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.Hypercube< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Addable< U > >.join(), random_hypercube(), frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.Hypercube< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Addable< U > >.slice(), and frodo2.solutionSpaces.UtilitySolutionSpace< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Addable< U > >.slice().
◆ testSmartJoinRandom() [1/2]
| void frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.tests.HypercubeTest.testSmartJoinRandom | ( | ) |
Tests the additive join method that automatically computes the variable ordering.
References testSmartJoinRandom().
Referenced by testSmartJoinRandom(), and testSmartMultiplyRandom().

◆ testSmartJoinRandom() [2/2]
| void frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.tests.HypercubeTest.testSmartJoinRandom | ( | boolean | addition | ) |
Tests the join method that automatically computes the variable ordering.
- Parameters
-
addition trueif utilities should be added,falseif they should be multiplied
References frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.Hypercube< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Addable< U > >.changeVariablesOrder(), frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.Hypercube< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Addable< U > >.join(), frodo2.solutionSpaces.UtilitySolutionSpace< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Addable< U > >.join(), frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.Hypercube< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Addable< U > >.multiply(), frodo2.solutionSpaces.UtilitySolutionSpace< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Addable< U > >.multiply(), and random_hypercube().
◆ testSmartMultiplyRandom()
| void frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.tests.HypercubeTest.testSmartMultiplyRandom | ( | ) |
Tests the multiplicative join method that automatically computes the variable ordering.
References testSmartJoinRandom().
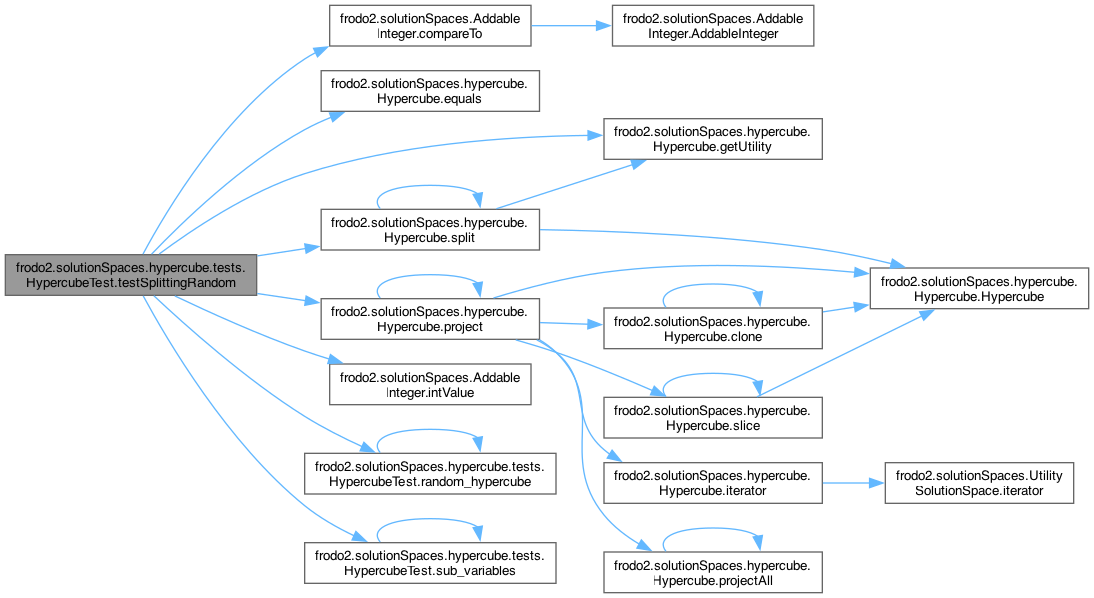
◆ testSplittingRandom()
| void frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.tests.HypercubeTest.testSplittingRandom | ( | ) |
this method creates a random hypercube.
then project the hypercube into a random a set of its variables and split the resulting hypercube then it compare the result with the one obtained when splitting first
References frodo2.solutionSpaces.AddableInteger.compareTo(), frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.Hypercube< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Addable< U > >.equals(), frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.Hypercube< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Addable< U > >.getUtility(), frodo2.solutionSpaces.AddableInteger.intValue(), frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.Hypercube< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Addable< U > >.project(), random_hypercube(), frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.Hypercube< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Addable< U > >.split(), and sub_variables().
◆ testUnion()
| void frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.tests.HypercubeTest.testUnion | ( | ) |
Tests the union() method.
References frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.Hypercube< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Addable< U > >.union().

◆ union()
|
private |
Computes the union of two lists, respecting the input total order on the elements.
- Parameters
-
array1 the first list array2 the second list total_variables the desired total order on the elements
- Returns
- union of the two input lists
References union().
Referenced by testProjectionRandom(), and union().

◆ verifyProjection()
|
private |
Verifies the output of the projection method.
- Parameters
-
hypercube the initial hypercube projOutput the result of the projection vars the variables projected out
References frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.BasicHypercube< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Serializable >.getUtility(), and frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.Hypercube< V extends Addable< V >, U extends Addable< U > >.getUtility().
Referenced by testApplyProjectRandom(), testProjOutputRandom(), and testProjOutputRandom2().

Member Data Documentation
◆ inf
|
static |
This variable is used to make sure that one does not mix plus infinity and min infinity in the testing.
Referenced by random_hypercube(), setUp(), testCompose(), frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.tests.HypercubeIterBestFirstTest.testMaximize(), and frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.tests.HypercubeIterBestFirstTest.testMinimize().
◆ maximize
| boolean frodo2.solutionSpaces.hypercube.tests.HypercubeTest.maximize |
This variable is used to choose between maximising and minimising during the tests.
Referenced by setUp(), testApplyProjectRandom(), testBlindProjectRandom(), testConsensusWeighted(), testProjectAllRandom(), testProjectionRandom(), testProjOutputRandom(), and testProjOutputRandom2().
The documentation for this class was generated from the following file:
- src/frodo2/solutionSpaces/hypercube/tests/HypercubeTest.java